What is Encryption?
Encryption is a method of encoding information in code to make the process inaccessible for those without a key. One of the basic strategies in digital security, encoding the information to an undecipherable from (ciphertext) using the power of the mathematical algorithms that are freaking complicated is a method which is not new in the sense that it has been exercised and seen as a way of securing data over the years but it is the most trouble-free approach available.
The secret to the frustrations of the attackers is thus achieved through the points that the text becomes unreadable for most of the people in the case of a breach and data confidentiality and integrity can be achieved by encrypting the data before it is transmitted to a receiver, which then makes it unreadable to other people, especially attackers.
Why Do We Use Encryption?
Encryption solves the following problems that occur in the digital sphere:
- block the unauthorized access to sensitive information
- ensuring privacy of the data being transferred through networks
- keep the sanctity of the stored data on the devices and cloud
- rely on the authenticity evidence of the D.C. data
- fulfillment of the data safeguard laws as well as industry standards
Encryption helps us as a society to provide privacy and security in a world that is quickly transforming into a digital society.
How Does Encryption Work?
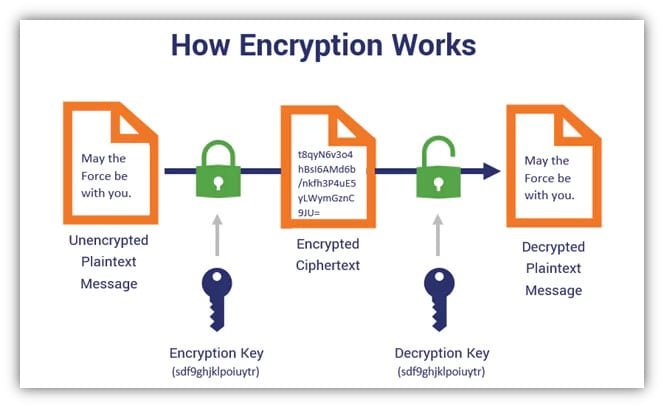
The encryption process is basically the mixing of several stages:
- In fact, in the first step, an encryption algorithm is chosen which actually runs the mathematical calculations and quickly produces an entangled code.
- The user generates or selects the key.
- Algorithms and keys are utilized for transforming the text to ciphertext.
- The resultant ciphertext is then sent to a receiver or saved.
- Using the corresponding key, the recipient decrypts the ciphertext to plaintext.
Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption
There are two types of encryption that are popularly used:
Symmetric
It is the use of a single key for both the encryption and decryption processes. However, this is the faster process but the exchange of the secure key is a must.
Asymmetric
It involves one pair of keys: a public key that is used in the encryption process and a private or secret key that is used in the decryption process. It is more secure for key exchange but it is slower for larger amounts of data.
What Are Some Common Encryption Methods?
Some of the used data protection methods are as follows:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)- Government and commercial applications use the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) (128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit key sizes).
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)-Widely used for securing web communications, email encryption, and digital signatures.
- Twofish & Blowfish- Secure and flexible alternatives, often used in file encryption.
- 3DES (Triple DES)- An improved version of DES, using three rounds of encryption for better security.
- Diffie-Hellman – Used for securely exchanging cryptographic keys over public networks.
- The Secure Hash Algorithm, or SHA-256, is utilized in password hashing and blockchain.
How Do We Use Encryption in Everyday Life?
And each of that becomes by far the most abstract level of everyday life as imagined today with a hater tip to the future of work and play. Transmission Security (HTTPS) is a significant way to enforce security on the web. Mobile Data Security is another mode where encryption is non-discrete. E-mail security and safety are also enhanced by the use of encryption. Virtual Private Networks (VPN’s) like Tor and VPN Private are responsible for the safe-passed e-mail and websites that allow users to connect to other basic sites without getting their IP address hacked. Digital signatures are not also left behind.
- Secure website connections (HTTPS)
- Mobile device security
- Email encryption
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
- Digital signatures
- Secure messaging apps
What Are the Challenges/Limitations of Encryption?
Even though, there are a few beneficial spots, for encryption it still has to confront the challenges it was traditionally challenged with:
- In a digital world, the management of keys adds a lot of difficulties. In order to protect encryption keys, one type of modern HSMs (Hardware Security Modules) may be used.
- System performance issues are another troublemaker that needs attention. Encryption always brings additional overheads.
- Encryption backdoor debates are a prevalent issue in government data privacy arguments. Tech companies argue that there.
- You risk permanently losing access to your data if you misplace your encryption keys.
- Keep an eye out for malware and phishing attempts; encryption cannot prevent them.
How Can You Stay Safe with Encryption?
In order to make sure you do not become a victim of any scam, follow this:
- Have strong, unique passwords and don’t use the same password across many different accounts or sites.
- Enable multi-factor authentication.
- Keep your software up to date – they should update automatically as soon as new versions are released.
- Use only reputable encryption tools such as those provided by trustworthy companies.
- Avoid sharing any sensitive data online if in doubt.
- Select a reliable, no-log VPN service.
- When storing sensitive data on USB devices, use encrypted disks.
Through our comprehension and proper use of encryption, we can definitely help to make this digital world a safe place for everyone.
Conclusion
A vital security feature, encryption ensures confidentiality and integrity of data by transforming it into an unintelligible format. Asymmetric encryption (safe, public-private key pairs) and symmetric encryption (quick, single key) are the two main categories. Data integrity is guaranteed by hashing algorithms like SHA-256 and bcrypt, while popular encryption techniques include AES, RSA, and ECC.
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA), VPNs, strong passwords, and end-to-end encryption (E2EE) at all times to keep safe. It is advised to use SFTP or FTPS instead of conventional FTP for secure file transfers. As cyber dangers change, encryption continues to be a crucial safeguard against data breaches and illegal access.



